How keyword cannibalization can affect your business?
Aloha, friends! In this article, we will delve deeper into the concept of keyword cannibalization and why it’s detrimental to your company’s website.
On corporate websites (and not only), it’s often noticed that there are pages on the same topic containing similar, and sometimes identical, keywords.
And there are reasons for this:
● Series of articles. If the topic is complex and you don’t want to create a huge block of text.
● Desire to cover the greatest number of keywords.
● Different content formats to increase the reach of the target audience.
The main problem is that with the wrong approach, you are likely to achieve the opposite effect. An excess of identical keywords on different pages can lead to their cannibalization. As a result, the ranking (authority) of your pages in search engines will drop, affecting your positions in SERP and organic traffic.
Keyword cannibalization is…
Keyword cannibalization occurs when content on different pages of your site ranks for the same cluster of keywords with the same intent. Keywords literally “compete” with each other, reducing effectiveness and hindering the pages and the site from reaching the top of SERP.
To understand this, let’s consider a simple example.
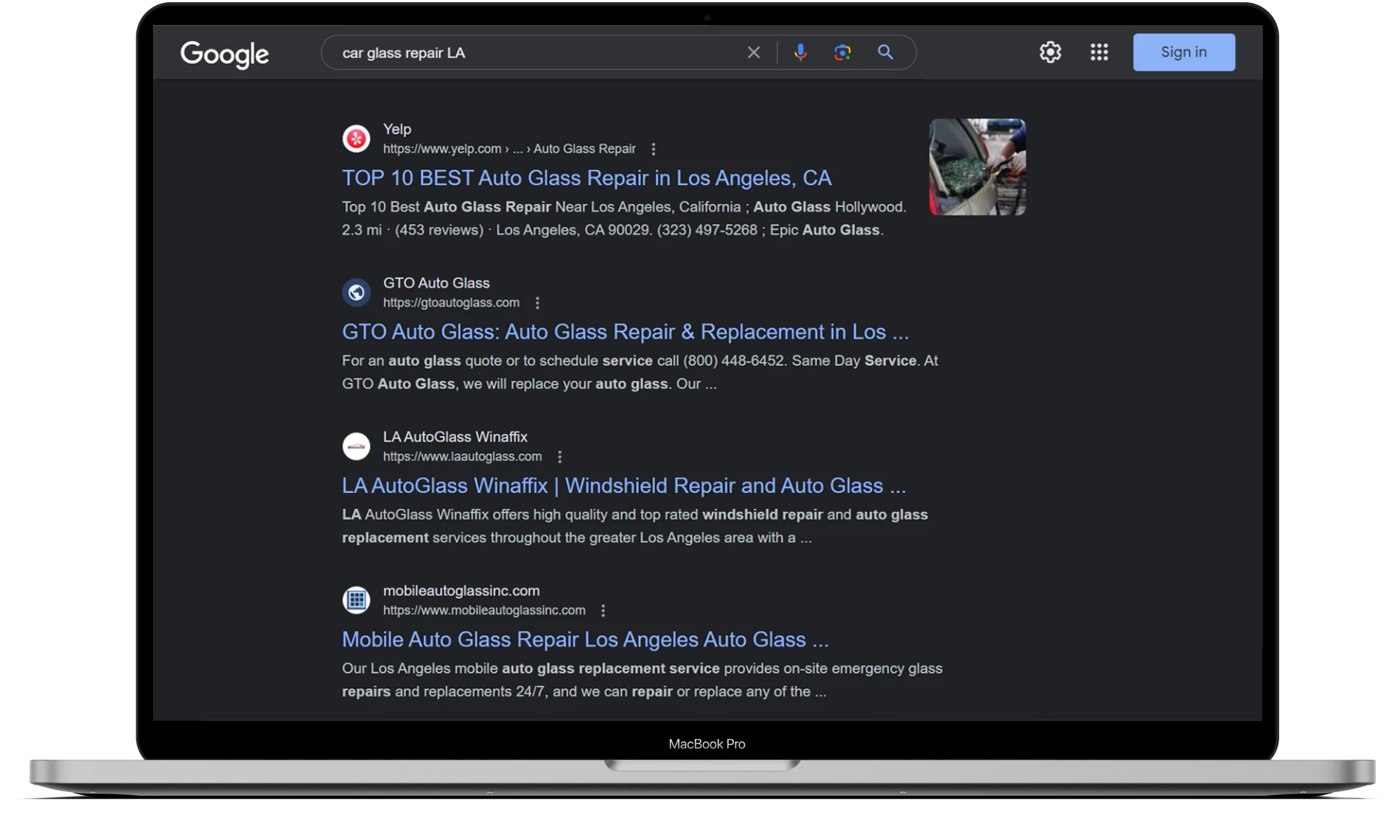
Imagine you have a car repair website. You offer services such as engine repair, bodywork, glass replacement, maintenance, and so on. It’s naturally more effective to optimize each page of the site for a single main keyword.
For example, a page offering glass replacement services should be optimized only for the keyword “car glass replacement”, while a page with engine repair services should be optimized for “car engine repair”.
However, what often happens is that pages are created for different car segments (expensive, cheap, etc.), but no one pays attention to the keyword set. This results in several pages being optimized for the same keyword, ignoring the page type, service type, and the user’s ultimate goal.
As a result, search engines might consider all your pages more or less equivalent. What’s even worse is that, essentially, you are entrusting the choice of the page for the keyword cluster to a search engine with its algorithms.
In practice, it looks like this:
You have a blog post describing the differences between types of car glass, but you also have a page for glass replacement services optimized for the same query
If you want the service page to rank higher in priority and attract traffic, find ways to differentiate these pages. For example, explore alternative keyword options within a similar cluster and optimize the article for them.
Otherwise, search engines will perceive these two pages as similar and they will compete with each other. If the blog page is better optimized (intentionally or not), it will outperform the service page and rise higher in the SERP, capturing all the primary traffic for commercial intent keywords.
It may even be necessary to sacrifice such an article (for example, by putting a <noindex> tag on it). Organic search results should match the user’s intent, especially when it comes to local businesses. The user is looking for a glass replacement workshop within their location, not an article about their options.
This means that, despite the good optimization of the article, it will never achieve good positions compared to competitors, as the page does not match the intent. By the way, regarding how to create SEO content correctly, you can read in our article.
How to detect cannibalization
Method one (basic)
In fact, it’s easier than it seems to detect cannibalization on your site. Simply use Google and search for “yourdomain.com, target keyword.” Going back to the previous example of car repair, it will look something like this:
As a result, you’ll see a list of pages ranked by relevance. For the sake of the experiment’s accuracy, it’s best to use incognito mode in your browser to ensure that the search results are not personalized.
*Note.
The method described above is suitable if your site doesn’t have too many pages; otherwise, this simple action will turn into a routine, and the effectiveness of the actions will decrease.
Method two (advanced)
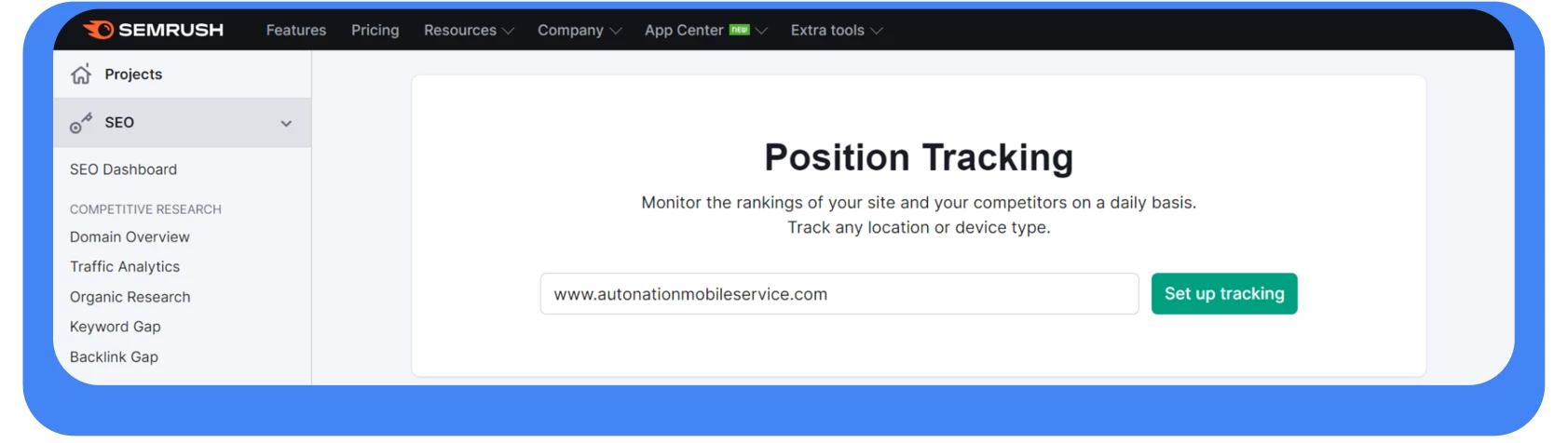
The second method is more advanced and automated, but it requires the use of the Semrush service. Within the service, there is a tool called Position Tracking, and that’s what we will use.
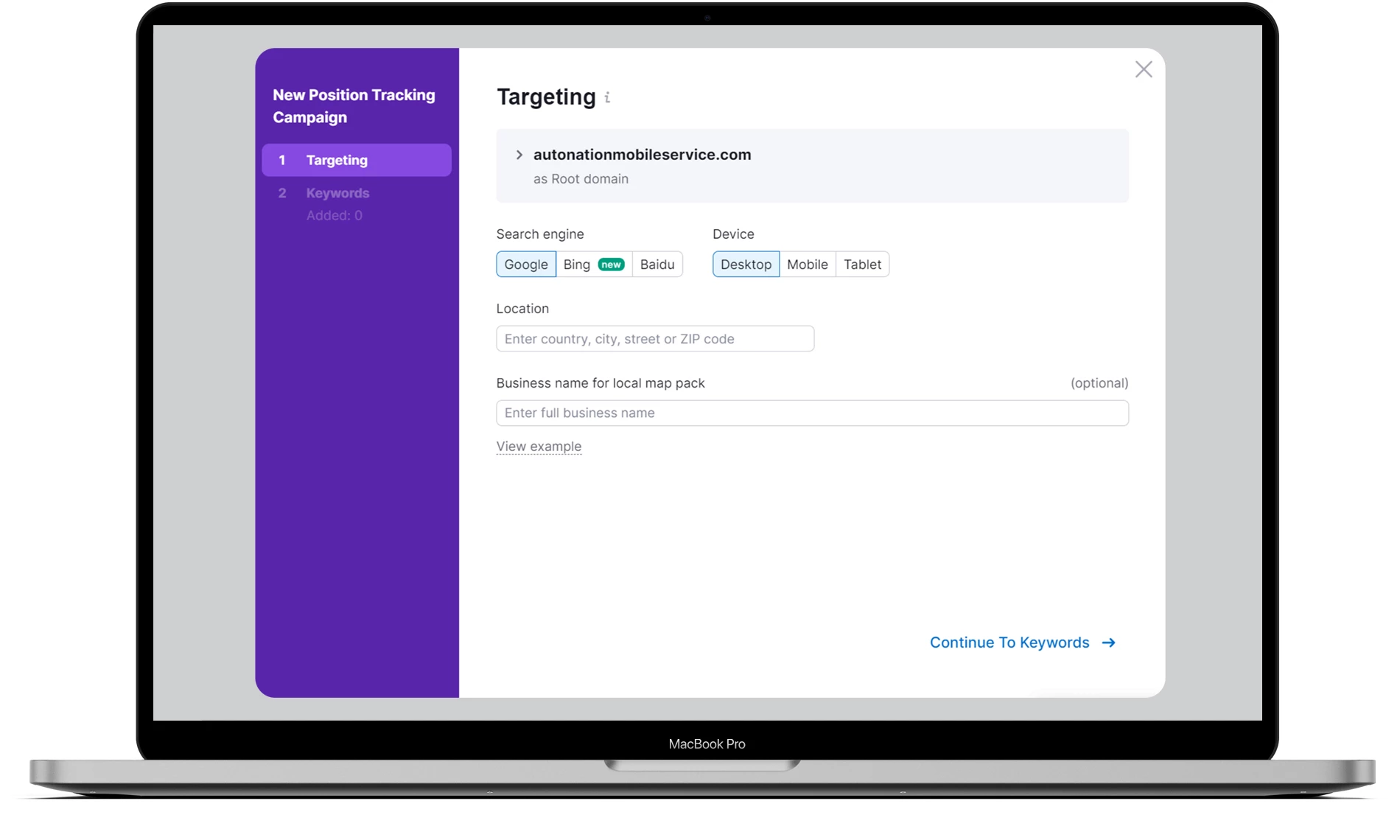
Enter the URL of your website and click on the “Set up tracking” button. Now for the basic settings: location, device type, search engine. In our case, it’s Google, the United States, Mobile.
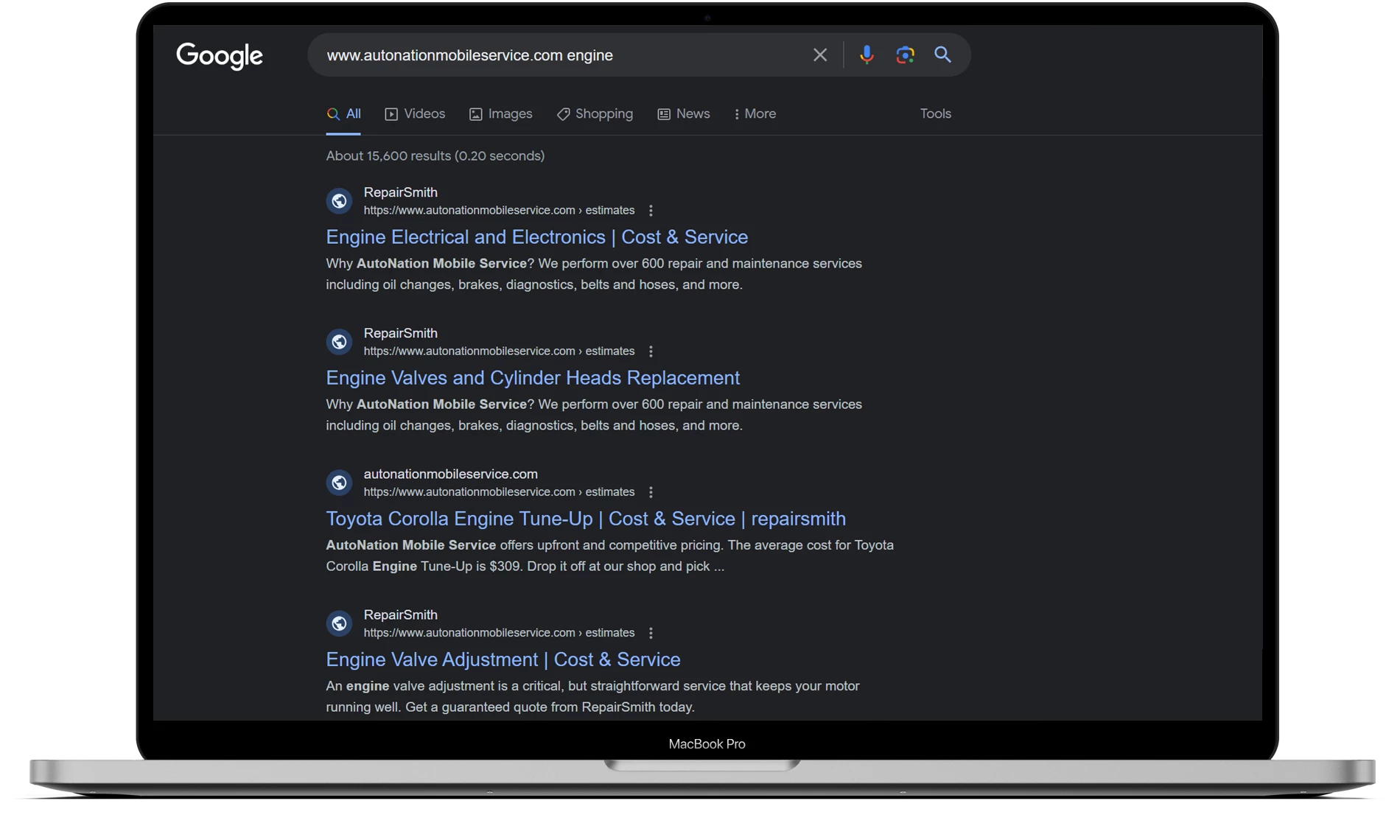
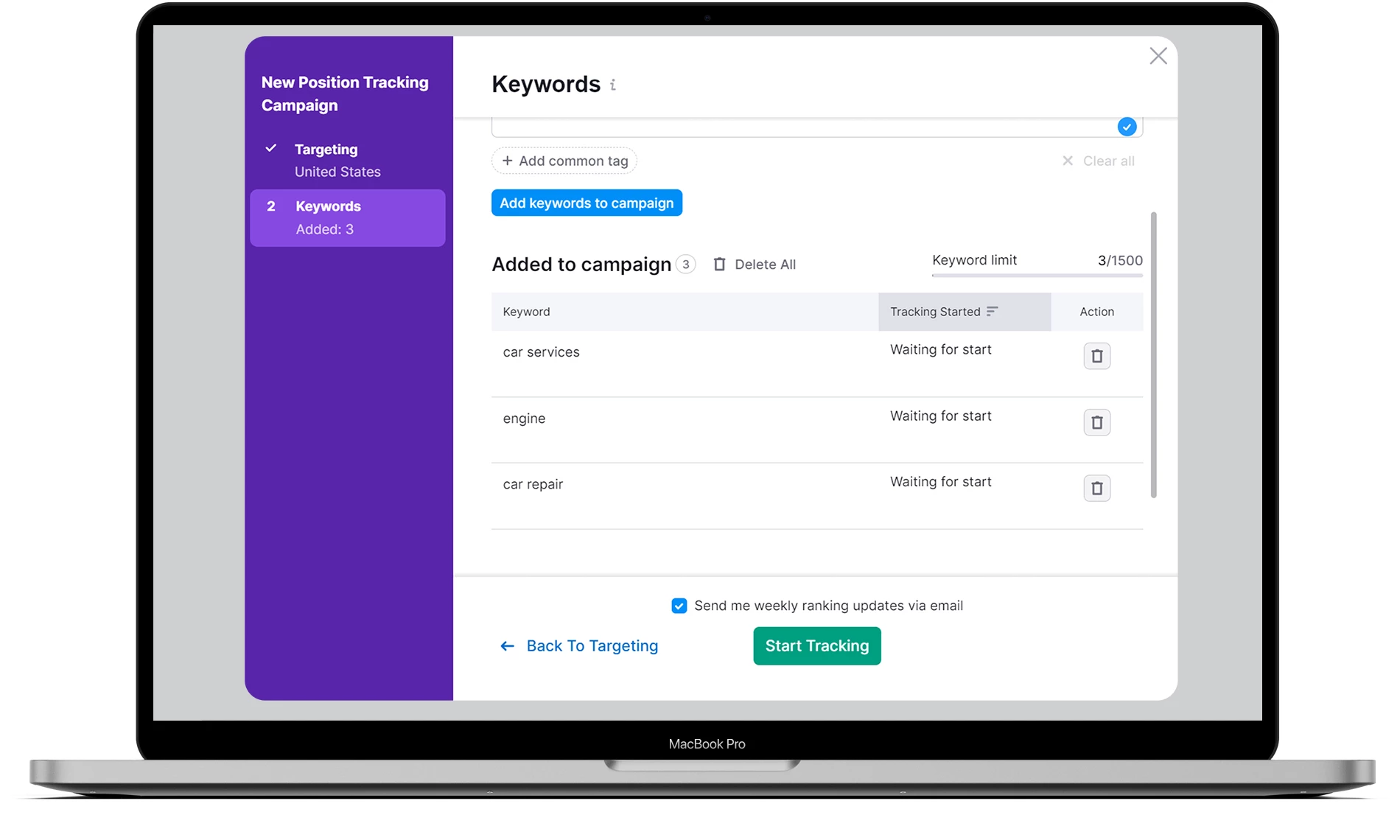
Next, you will need to specify the keywords that will be used for position tracking. For example, let’s take a simple set: car repair, car services, engine. Add them to the campaign and start tracking.
All these actions are necessary in order to access the report on keyword cannibalization in the tool.
Once we have access to it, we can immediately see which pages are capturing the keywords we need and whether they are ranking as needed in the SERP. Of course, it’s possible that several pages for the same keyword are ranking at a very high position in the search results.
To definitively answer the question about cannibalization, it’s necessary to understand whether these pages satisfy the same user needs.
Eliminating keyword cannibalization
Here are a few recommendations to help you address cannibalization on your pages:
1. Consolidate content.
Carefully review the content that is on the “cannibalizing” pages; it may be possible to consolidate it into a single page. For example, if you have two top-performing pieces that can complement each other, it’s better to update the original article and expand it.
2. Remove content.
This method is extreme and is recommended only if the content is no longer needed. In this case, you would delete the page or publication and reallocate the content strategy based on your needs.
3. Remove keywords.
This method requires manual intervention and can be time-consuming, but it is relatively straightforward to implement. It’s suitable if the keywords will not compromise the quality or meaning of the content on the page.
4. Internal linking
Organize internal links on your site so that less significant content links to more important and relevant content. This action signals to search robots that this content is more important.
5. External linking
Unfortunately, the reasons for keyword cannibalization may not always be within your control. External links are one such example. Less relevant pages may rank higher in SERP due to external links from more influential sources.
For example, you write an article on a popular topic, and a major news website links to your piece as a source in their publication. To address this situation, you will have to personally contact the webmaster responsible for that site to request the removal or replacement of the links.
*Additional information:
To track all external links, you can use specialized services or the free Google Search Console web analytics tool.
What about practical application?
To understand the full extent of the problem, let’s look at a case study from our Keyword Insights colleagues.
In short: They identified a traffic cannibalization issue on the large real estate service ZeroDown.com, fixed it, and increased organic traffic by 110%.
The client set the initial task of achieving the highest positions to generate more organic traffic, but the problem was that the service contained over 50 million pages.
Here are some of the queries for which ZeroDown wanted to generate more organic traffic:
● Homes for sale in California
● Houses for sale in California
● Properties for sale in California
● Homes for sale in Las Vegas
● 2-bedroom homes for sale in Florida
● 3-bedroom houses for sale in Florida
● Log cabins for sale in Boulder
● Wood cabins for sale in Boulder
● Mansions for sale in Los Angeles
● 9 bedroom houses for sale in Los Angeles
● Colonial homes for sale in Orange County
● Ranches for sale in Texas
● Beachfront condos for sale in Miami
● Apartments for sale in New York City
● Townhouses for sale in Seattle
The real problem:
Firstly, many city-specific search queries were stuck on the second page of SERP or even beyond the top 30.
Secondly, a large portion of the URLs (which, by the way, numbered in the hundreds of thousands) were marked in GSC as “crawled but not indexed.” Moreover, these often weren’t even the target pages that should have been in their place.
To identify the problem, the team began scanning the site but encountered failure. The scanning lasted for over two weeks, during which a malfunction occurred. As a result, only half of the original number of pages—25 million URLs—could be analyzed.
Why did this happen? It was all due to the internal structure of the service. A target page was created for different keywords under each type of real estate. Doesn’t sound so scary, does it?
However, the website has over 400 types of different real estate, and pages are created for each state, city, district, and zip code. As a result, millions of nearly identical pages are generated.
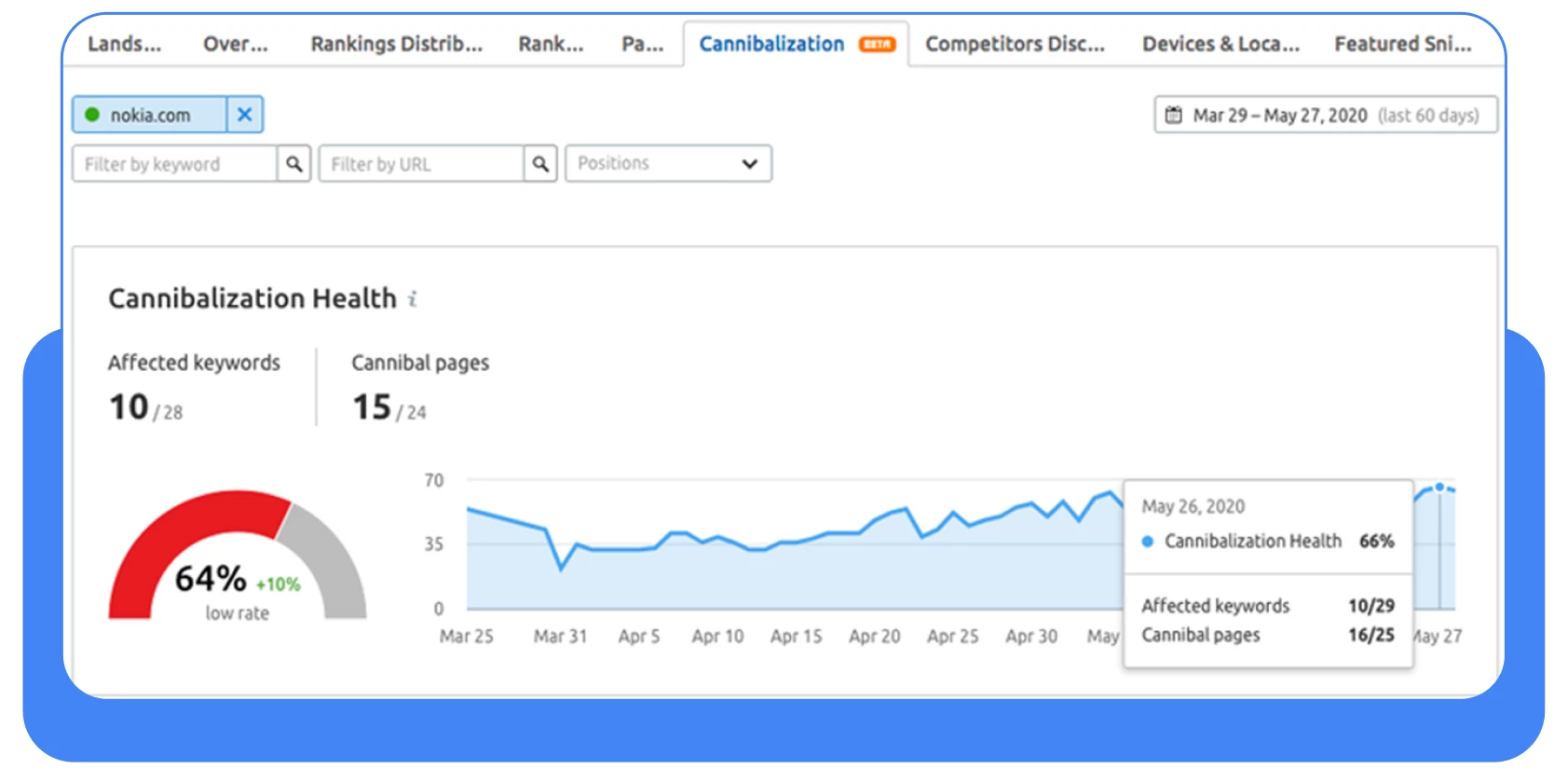
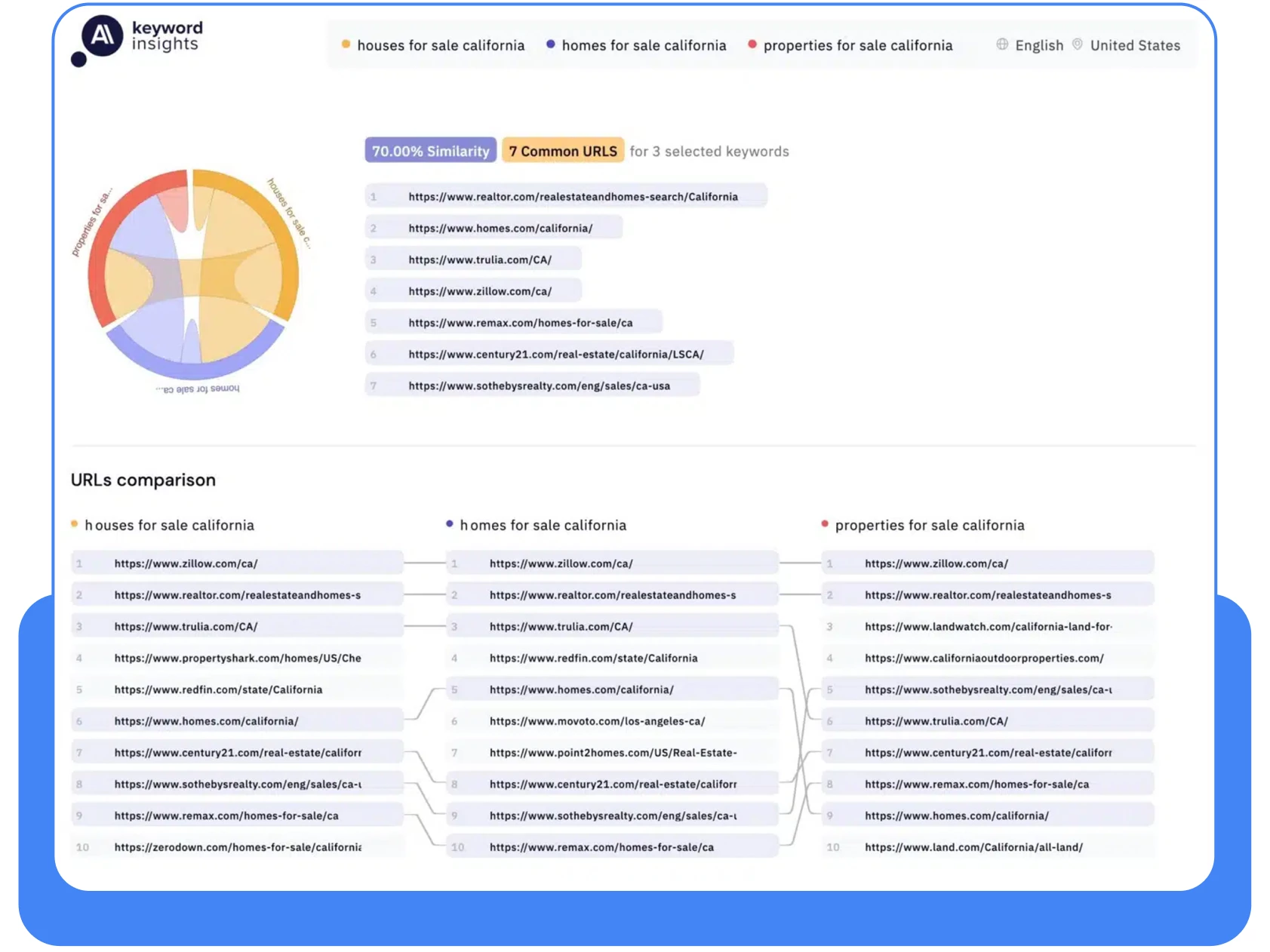
Next, the SERP results for similar queries were checked: “houses for sale in…,” “homes for sale in…,” and “properties for sale in…”. The similarity of such queries is over 70%; see the screenshot below.
How was it fixed?
The structure was redistributed, and keyword clusters were rearranged. With this approach, the number of property pages was reduced from 400 to 85, with the remaining URLs being consolidated.
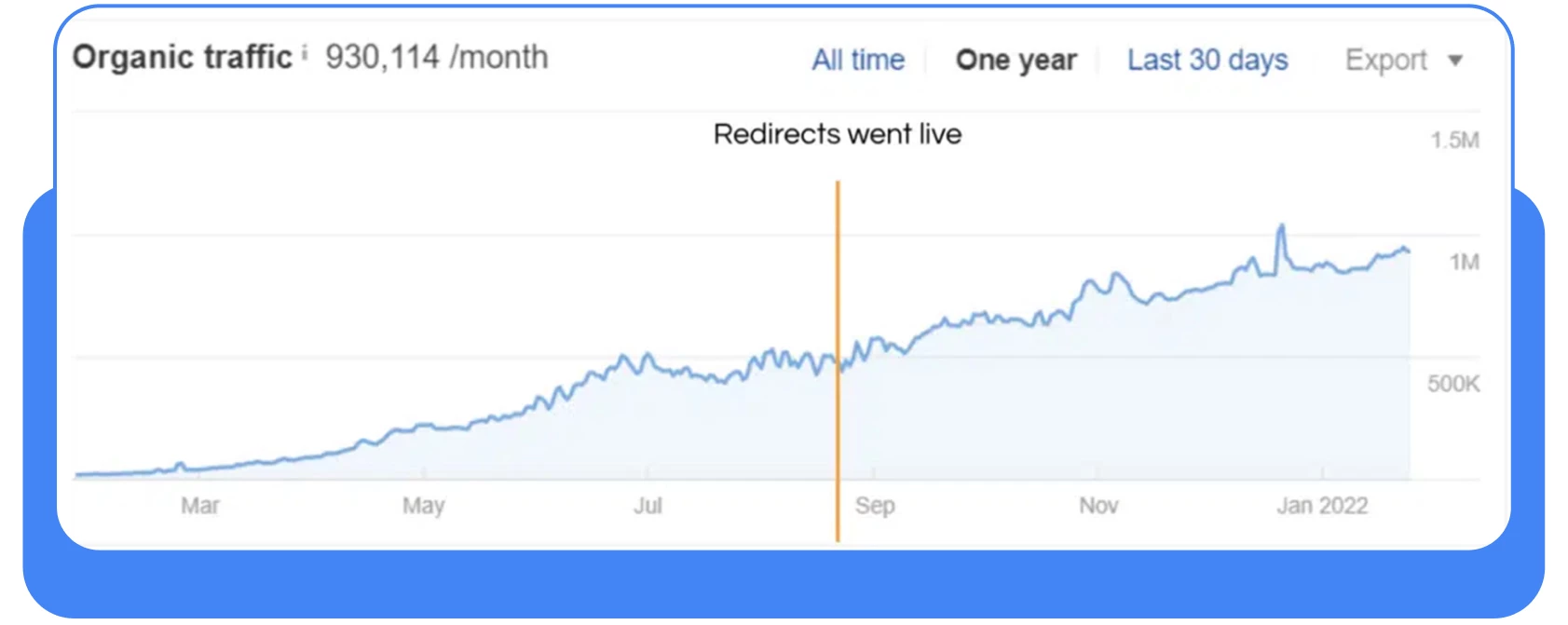
What was the result?
A 110% increase in organic traffic. A 110% increase is significant even for small informational websites, but in this case, the service gained an additional 500,000 visits to its site within a month.
Conclusion
Traffic cannibalization is a real problem that affects not only small websites but also large services. Avoiding this issue requires a well-thought-out site/service structure: URLs, subfolders, etc. As the saying goes, “prevention is better than cure.” Therefore, if you feel like you are not getting enough traffic to your site, it might be the case. Check whether keywords on your pages overlap and fix it.
Friends! We wish you all excellent organic growth. Share your experiences with keyword cannibalization in the comments; we would be happy to hear about your experiences.