How Does a Content Delivery Network (CDN) impact SEO?
Hello dear friends, SEO experts and enthusiasts! Today, we would like to talk about CDNs and their impact on traffic and, specifically, SEO.
In our article about multilingual websites, we mentioned that if your multilingual versions are hosted on a single server, users from distant regions may experience delays in accessing your site. To avoid such issues, it is recommended to use a CDN (Content Delivery Network).How to create a Multilingual website, why is it needed and how good is it for SEO?
A CDN is a distributed infrastructure of nodes (data centers and servers) worldwide, which selects the server closest to the user’s location for content delivery to reduce loading time.
In this article, we will delve into how CDNs affect SEO and the extent of their significance in doing so.
**********
What is a CDN and how does it work?
One of the most important factors for your SEO is the page loading speed of your website. This is especially crucial if you have a multilingual/multiregional site, such as an international clothing store or a high-tech service platform.
If you have a clear understanding of your company’s geographical presence, building a quality content delivery system is not so difficult. Let’s consider an example. John is a reseller of premium sportswear in Europe and Asia. His IT department informs him that 35% of his website visitors come from Singapore, Japan, and Korea. While John has localization for these regions, the loading speed is not up to par.
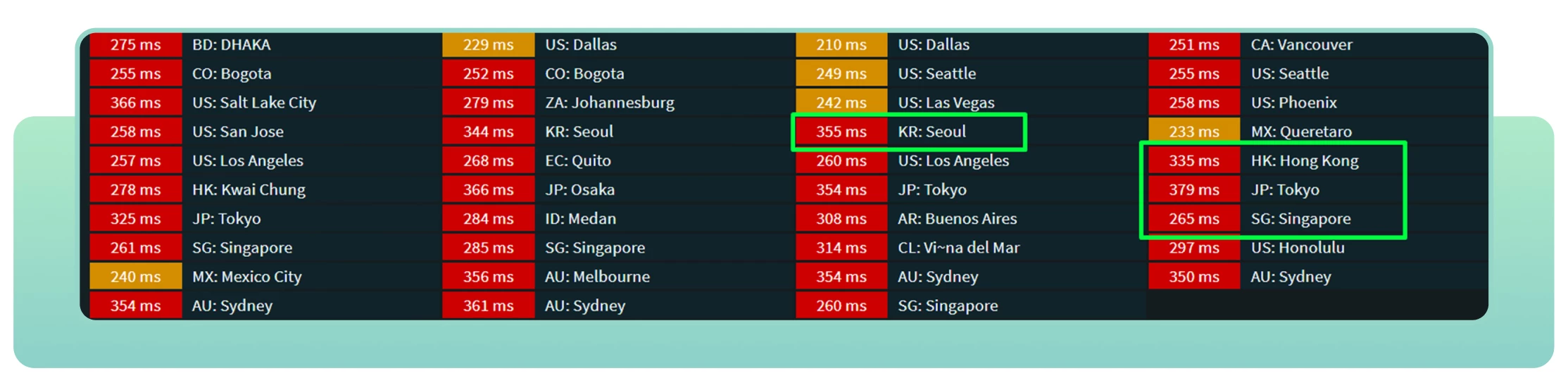
A good, albeit not entirely accurate, example would be pinging servers in the desired country. Let’s conduct an experiment in Amsterdam using mobile internet. We will ping all international servers, but our focus is specifically on Asia: Seoul, Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
The minimum delay is 260 ms to the Singapore server, and that’s just a simple transmission of a couple of packets back and forth. After seeing this less than ideal situation, John wonders what this CDN is all about and whether it can help improve the loading speed of his website in Asia
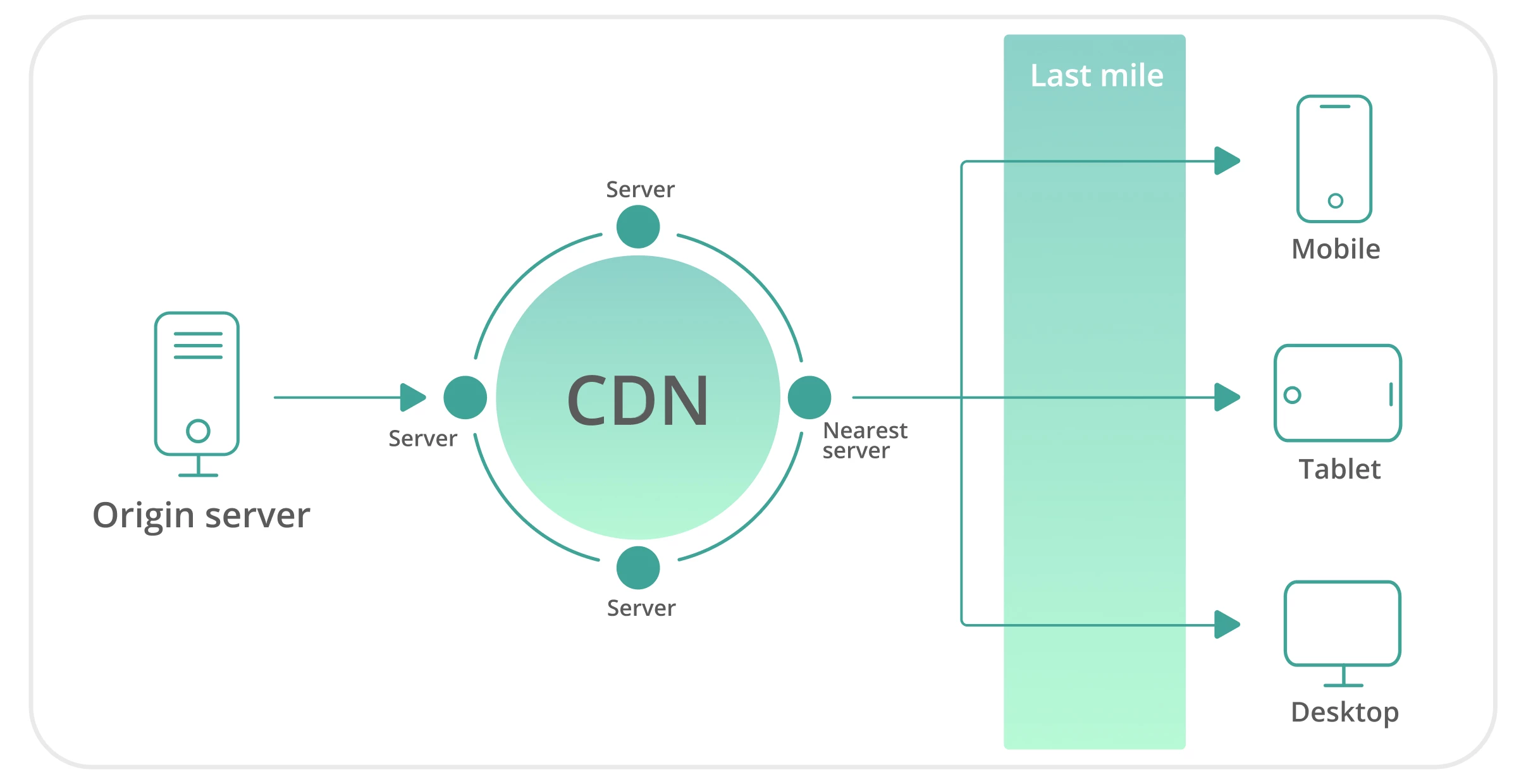
In practice, a CDN works as follows. When a user visits John’s website, luxesport.com, the website delivers the HTML page to them. However, all static and dynamic objects, such as CSS and scripts, will be referenced from cdn.luxesport.com.
In practice, a CDN works as follows. When a user visits John’s website, luxesport.com, the website delivers the HTML page to them. However, all static and dynamic objects, such as CSS and scripts, will be referenced from cdn.luxesport.com.
This means that your images, products, and other objects from your server are first transmitted to the nearest node to the user and then displayed to them, reducing latency. Regardless of the device a user chooses to access the site from, the data will be delivered not from your source server but from the CDN node.
By the way, one of the best examples of a good CDN, known to all engineers, is github.io. All data on the page is static and delivered to users from different regions through the CDN.
CDN Working Principle
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) operate based on three main principles:
- Caching
- Edge computing
- Acceleration of dynamic conten
Caching is the first principle of CDN, which involves storing multiple copies of your data on servers or devices for faster access. Within the CDN system, caching works as follows:
- A user from a remote region sends a request for your static content, which is hosted on your website.
- The source server responds to the user’s request and duplicates the response to the nearest CDN node based on the user’s location.
- The node, also known as a Point of Presence (POP), stores a cached copy of the data.
- The next time the same user or any other user from that region sends a request to your website, the data will be loaded from the node instead of the source server.
The next key aspect of CDN is working with edge servers within the content delivery network. To optimize server performance, specific logic is implemented between the CDN’s edge servers (POP) and the source server. For example, you can delegate tasks such as monitoring user requests or optimizing content before delivering it to users to the edge CDN servers.
And finally, the third principle is the acceleration of dynamic content. Caching dynamic content is not practical due to its constant changes. Additionally, sending a request with high latency can result in either timeouts or significant delays, which can disrupt the page rendering.
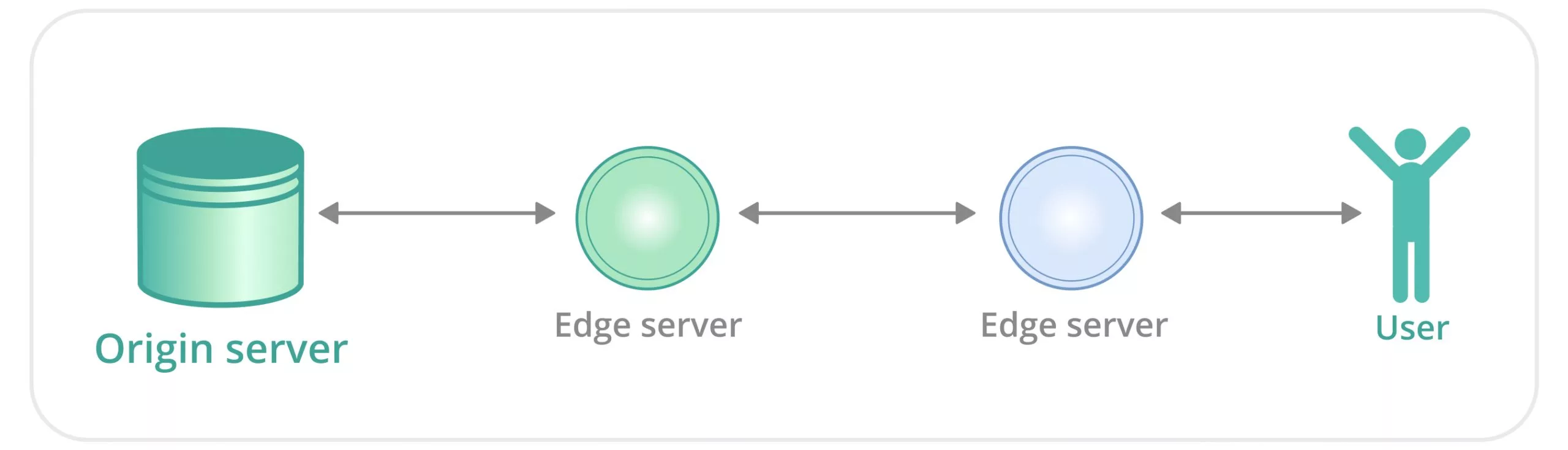
Therefore, a specific network rule is established: user — node — node — source server. In other words, a user’s request for dynamic content follows the scheme outlined below:
In other words, the dynamic content is transmitted from the source server to the nearest node, then through the CDN infrastructure to the closest node to the user, and ultimately directly to the user. This way, the content delivery system establishes a reliable connection between the server and the user.
What types of content can be delivered through a CDN?
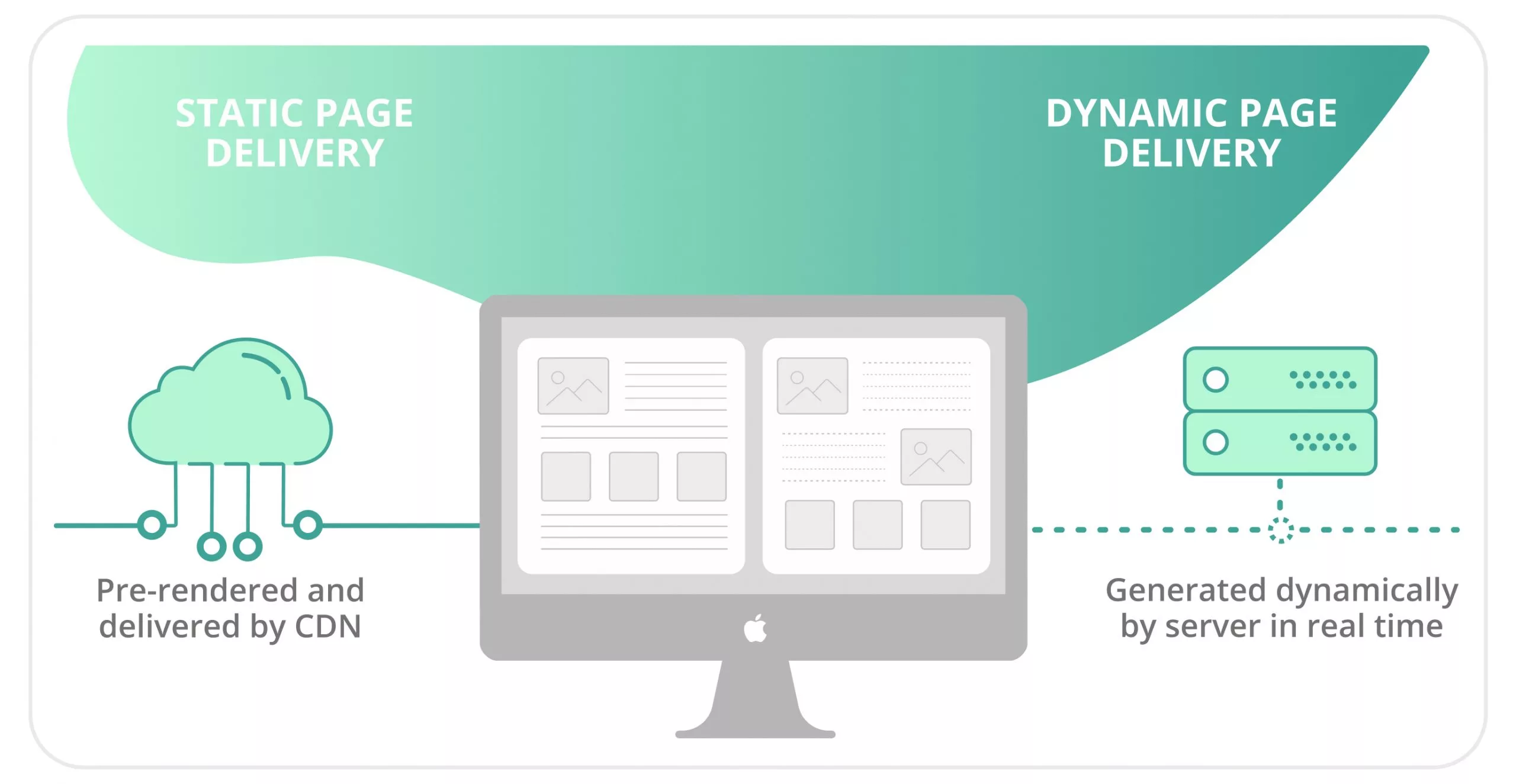
Both static and dynamic content can be delivered through a Content Delivery Network.
Static content refers to content that appears the same for all users, such as headers, images in the header, logos, and text styles. The advantage of static data is that it doesn’t require generation or processing, making its delivery much simpler.
Dynamic content, on the other hand, is the complete opposite of static content. Examples include weather forecasts, user profiles, and social media feeds. This type of content is personalized for each user based on various parameters. Your website generates such data separately for each individual user.
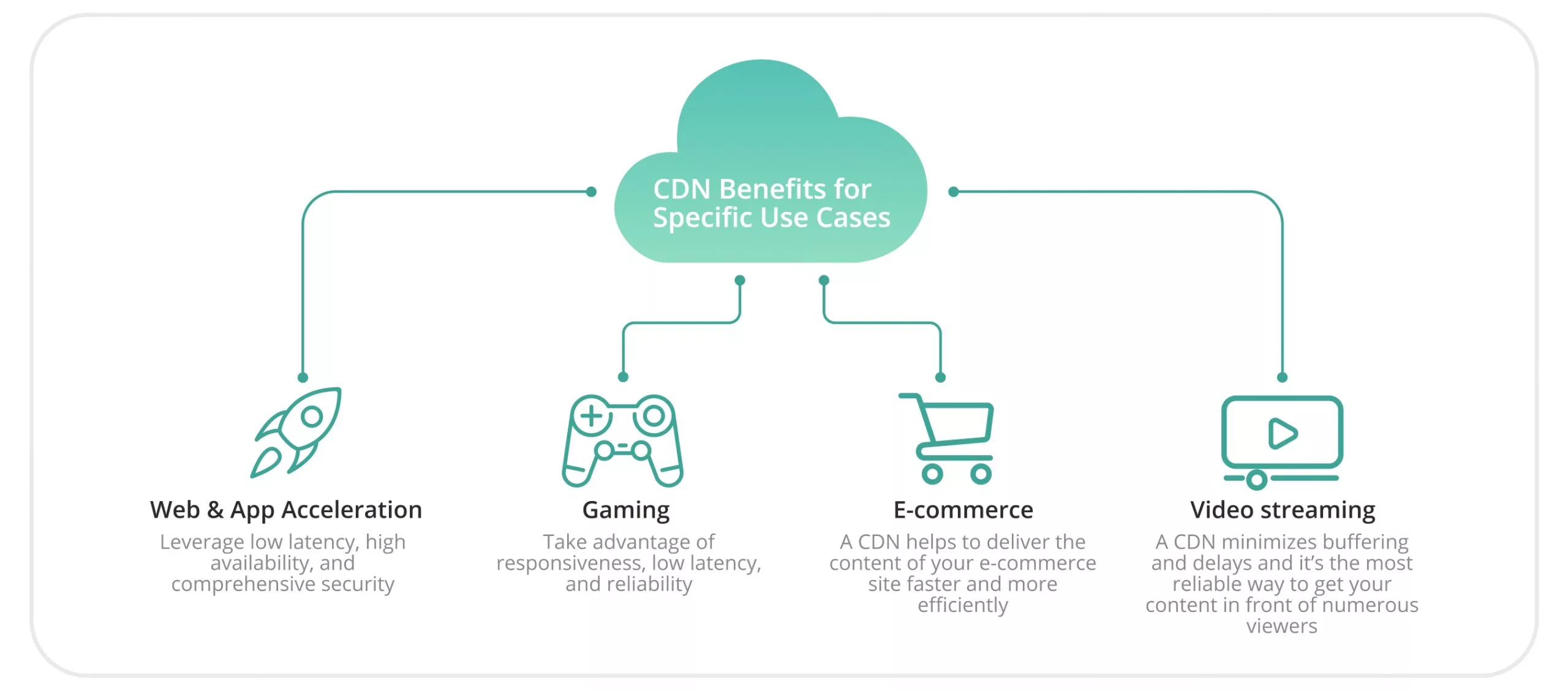
Task #1 — Swift content delivery
A great example is the Western news agency Reuters. Their task is to deliver up-to-date news to major news channels such as BBC, Washington Post, and others. Content delivery needs to be fast, reliable, and reserved.
Task #2 — Streaming media delivery
Nearly all audio and video streaming platforms utilize CDN networks to optimize content delivery. Examples include YouTube, Netflix, Hulu, Twitch, and Spotify. It’s not surprising as these services require channels capable of delivering content and monetizing it at speeds of up to 20 Gbps.
Task #3 — Scalability
This applies to social network games, streaming games, and other platforms that need to handle constant user loads. In Russia, a great example is VK Play, which uses a CDN network to distribute user loads and store data, ensuring access to the service from any device without losing progress. In the West, a notable example is NVIDIA’s cloud gaming service — GeForce NOW.
If you want everything to be done for you, welcome to outsourcing with us!
To delve into this topic, let’s first look at an interview with John Mueller (for those who may not know, John Mueller is a Senior Search Analyst at Google) dated June 3, 2022. In this interview, the impact of CDNs on search engine ranking positions (SERP) and overall SEO is discussed.
According to Mueller, CDNs do not have a direct impact on SEO, except for improving the speed in regions where the connection to your server is unstable or experiences high latency.
The same interview also raised the question of whether CDNs affect search engine crawlers. Mueller responded as follows:
If your server is too slow and its hardware cannot handle the constant scanning from search engine bots, both legitimate and non-legitimate, then a content delivery network can indeed alleviate the load on the main server. The majority of the data will be loaded from the CDN rather than the source server.
To summarize: Google maintains the official position that CDNs do not directly impact the SEO of your website. While CDNs can improve the speed of accessing your site and optimize server performance, they do not have a direct impact on search engine rankings.
**********
Some Interesting Statistics
Before we delve into real-life use cases of content delivery networks, let’s look at some interesting statistics.
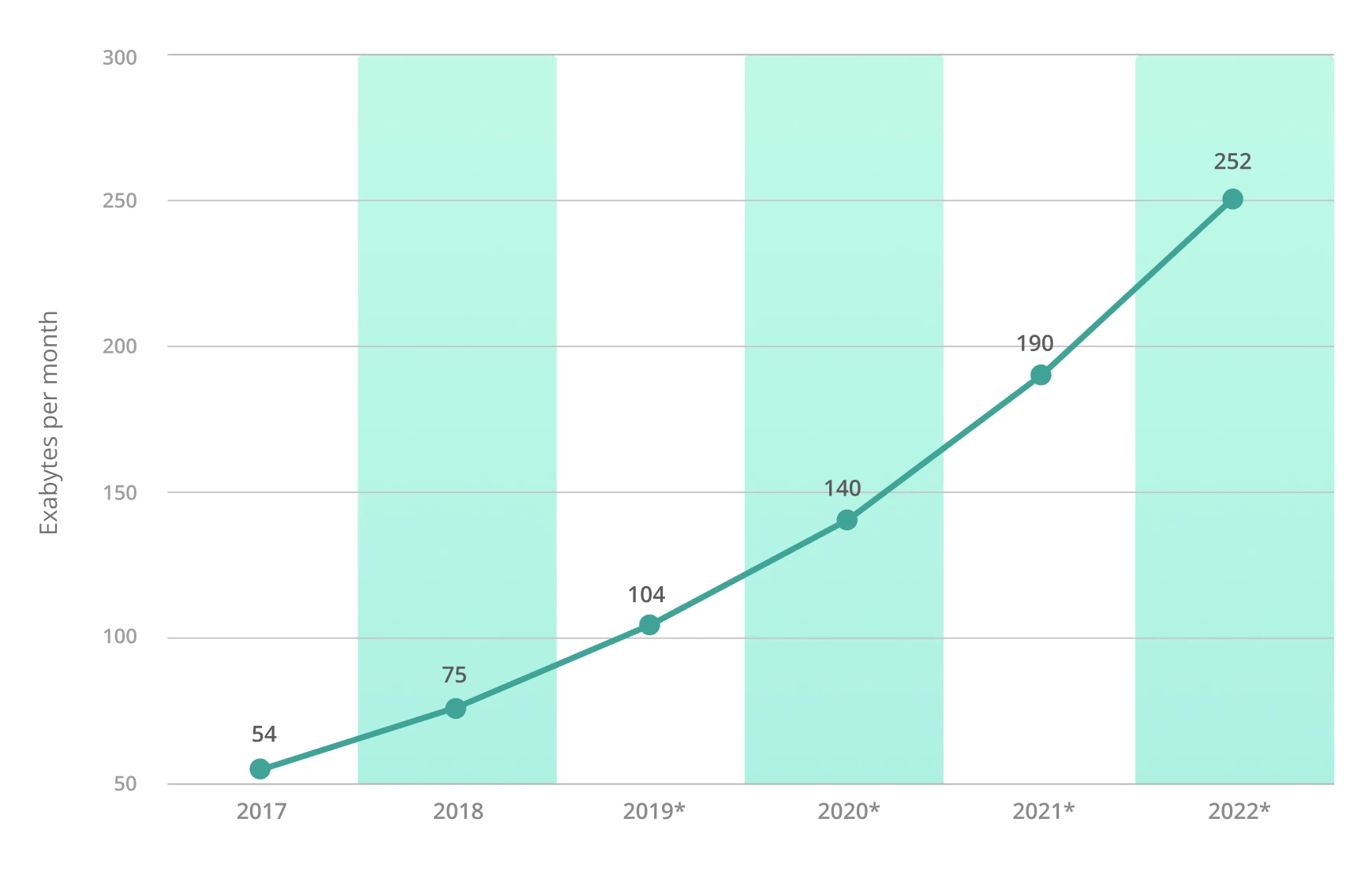
According to Statista, the volume of traffic passing through CDNs has been significantly increasing every year. In 2017, it was 54 exabytes, and by 2022, it had reached 252 exabytes.
For reference: 1 exabyte = 1,073,741,824 gigabytes.
So, 252 exabytes = 270,582,939,648 GB.
Impressive, isn’t it?
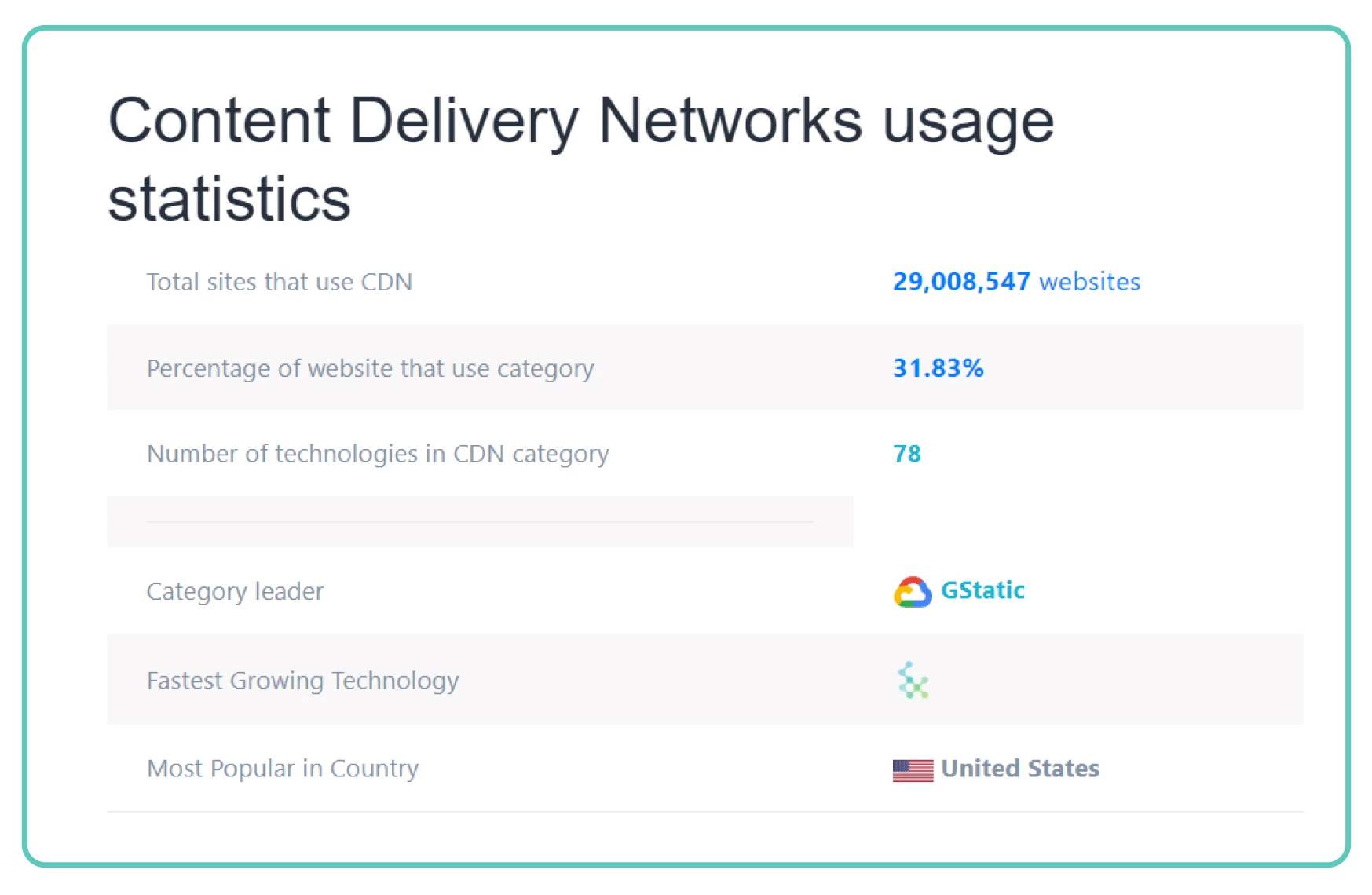
When it comes to the usage of CDNs, let’s turn to WebTechSurvey.
31% of websites worldwide use CDN technology to deliver content to their users. The technology is most popular in the USA, which is not surprising considering that the offices of giant CDN providers such as Amazon, Google, and CloudFlare are located there.
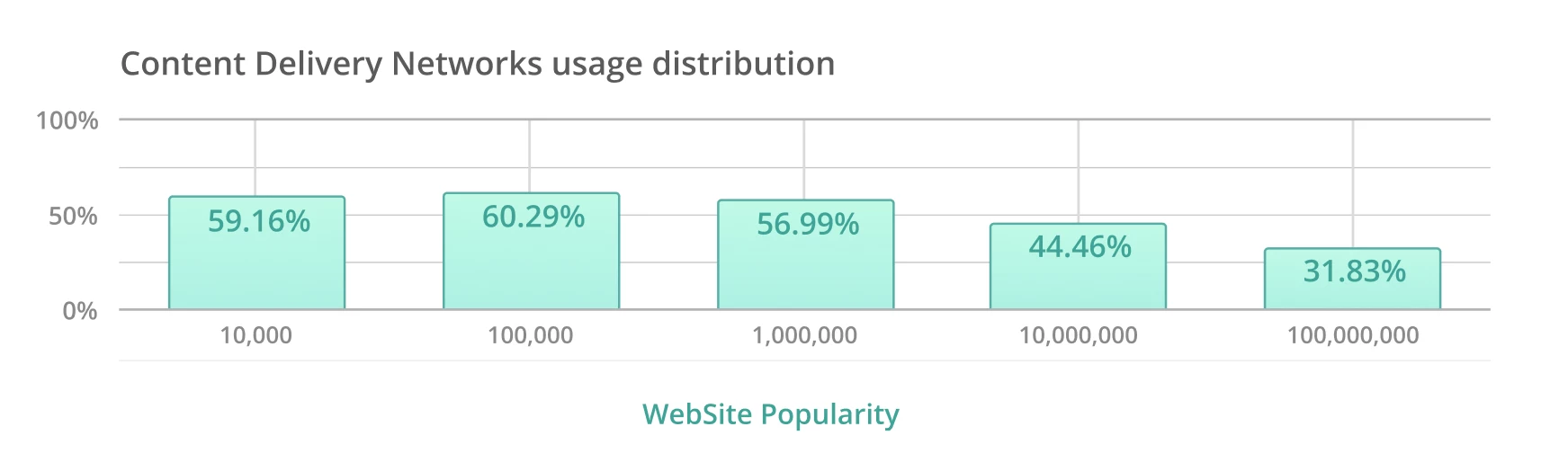
Now let’s look at the percentage distribution of popularity among websites, and the statistics are quite interesting.
It can be seen that the lag in adopting CDN technology begins only after the top 10 million websites.
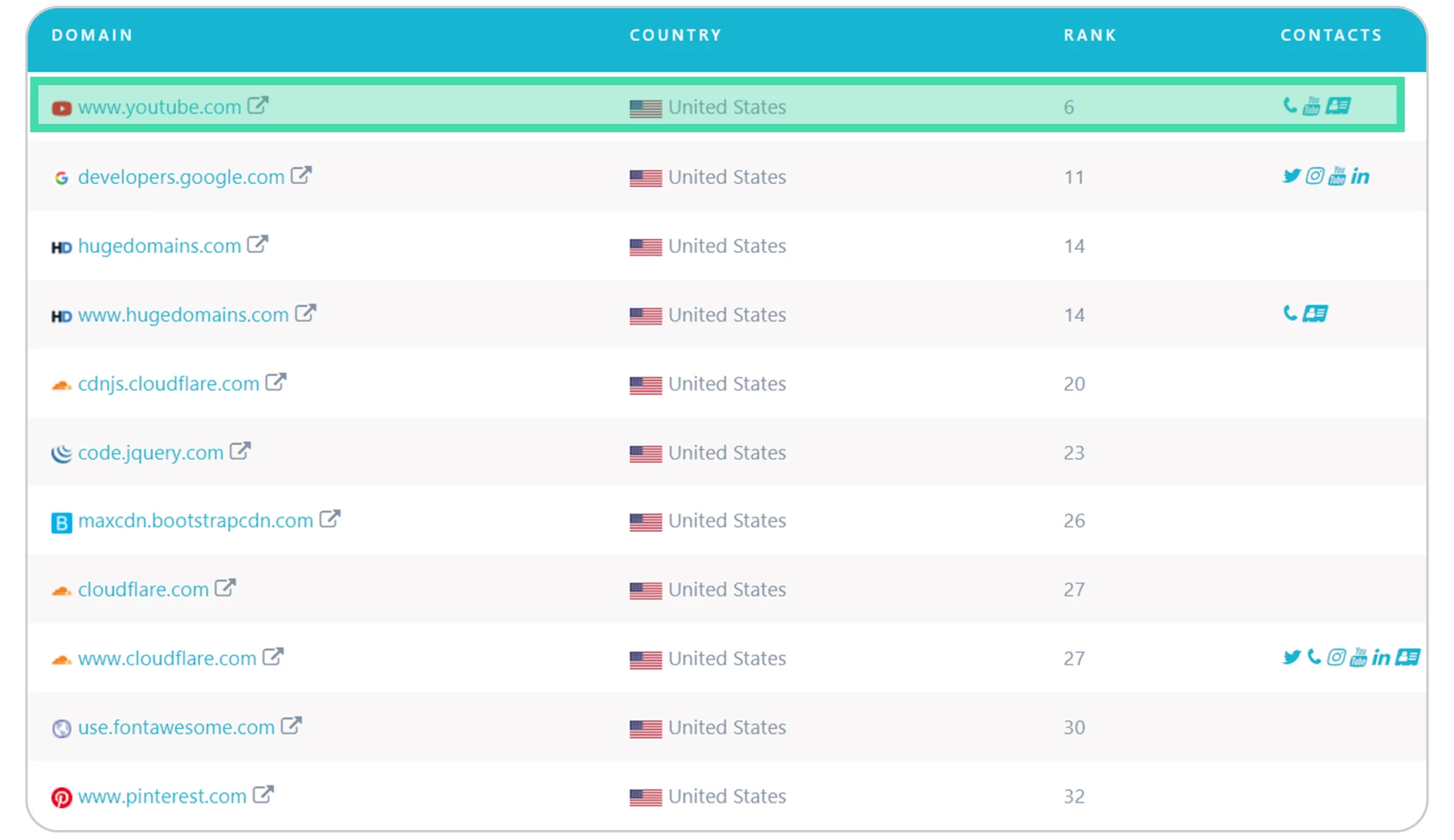
The most popular website using a Content Delivery Network is YouTube.
**********
Implementation Case Studies
Let’s consider some case studies of American CDN providers.
Case #1 — Barn2 Media is a small but promising company specializing in website development and plugins for CMS platforms like WordPress and WooCommerce.
Website development often involves using pre-designed themes and a set of plugins. This approach significantly reduces development costs and makes it more accessible for many small companies. However, it has one major drawback: low performance due to the CMS’s heaviness.
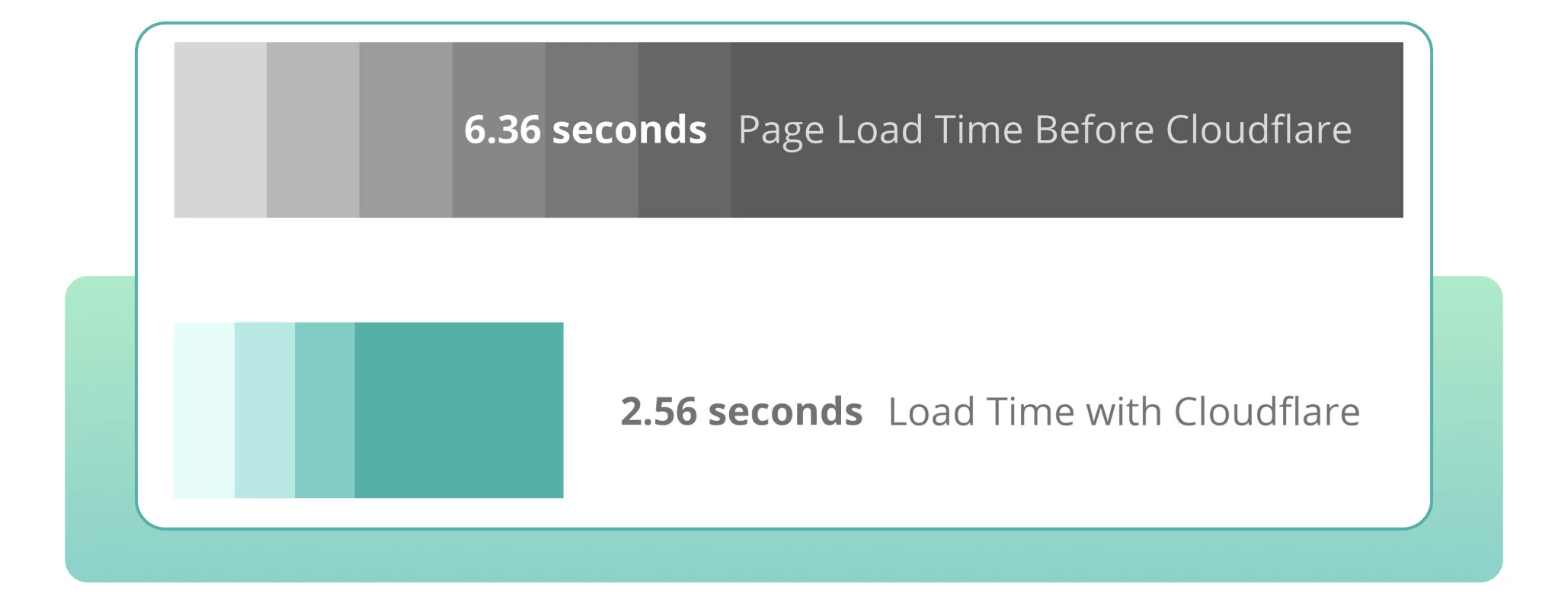
The average loading speed of such a website was 6.36 seconds, which is considered very slow and falls into the red zone. Naturally, this leads to higher user bounce rates and has a negative impact on SEO.
After implementing CDN architecture, the average loading time improved to 2.56 seconds. A quite satisfactory result
Case #2 — FCL/Gazeta Esportiva
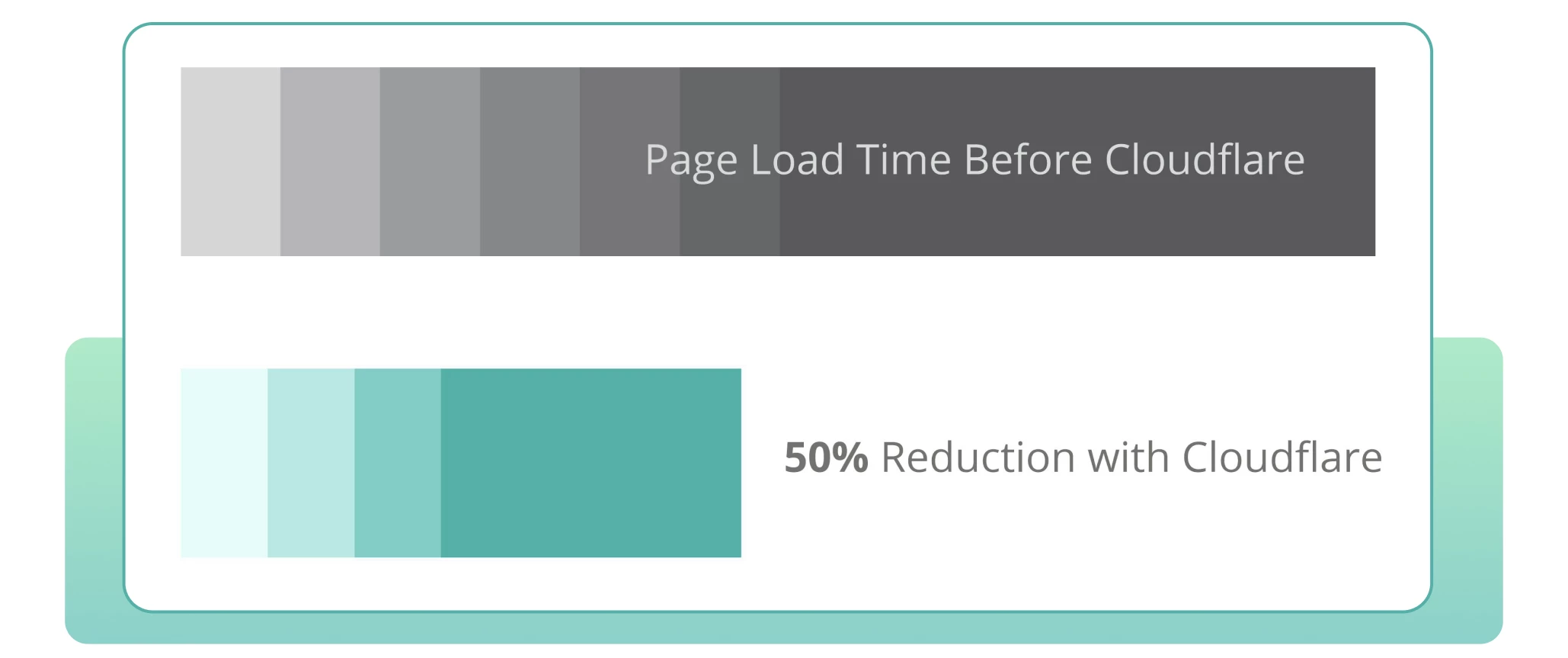
FCL/Gazeta Esportiva is a Brazilian publication with over 70 years of history. In addition to their website, they also have a radio station, TV channels, and a print edition. The company’s main goal was to expand their offline presence into the digital format.
After implementing the technology, the company was able to reduce loading speed by 50% and increase user retention.
Case #3 — FloSports
This case involves the implementation of a Content Delivery Network by stackpath.com.
FloSports is an online sports streaming service. Their goal was to create a serverless streaming infrastructure on a CDN for premium subscriptions.
They successfully built their own streaming network with a capacity of 65 Tbps, using 50 POP units worldwide. These statistics are comparable to other leading players in this field. In this CDN, not only CSS but also JS scripts and videos are delivered.
Over the course of a year, they were able to increase new subscribers by 125%, which is quite impressive for a startup.
**********
Conclusion
Despite Google’s ambiguous statement that CDNs do not impact SEO, most Western colleagues are confident that there is a correlation. CDNs have not only become an industry standard, especially in corporate SEO, but they also directly affect website loading speed, organic traffic growth (especially when creating multi-regional resources), and ultimately significantly improve the user experience.
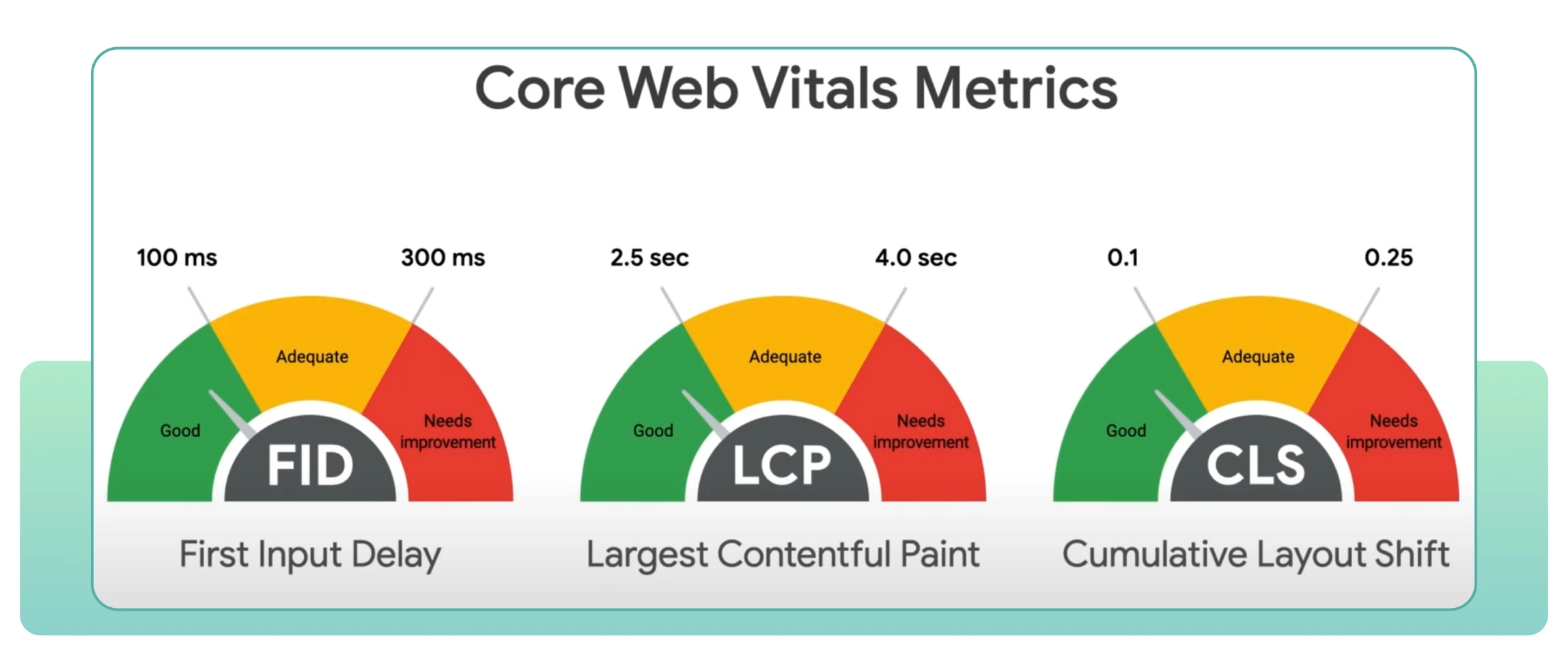
It is worth noting that almost every (at least publicly discussed) Google algorithm update in recent years has included elements aimed at improving page performance, increasing speed, and content delivery. This is particularly evident with the introduction of Core Web Vitals updates.
In conclusion, I would like to provide a few tips for choosing a content delivery network solution.
- Test the DNS response time between the edge node and the end user before committing to a costly implementation. It’s better to test this before investing heavily.
- If your organic traffic has seasonal variations, make sure to test the CDN’s responsiveness during those periods.
- Consider the connection time when selecting nodes and providers. Look for stable connections, minimal delays, and zero packet loss.
- Make sure to display cache statistics, at the very least the hit/miss parameters, on your dashboard.
- Ensure that the channel’s bandwidth is provisioned witha 20–30% buffer above your maximum volume.
- Consider the quality of the API. As your resources grow, you will likely need to customize the infrastructure to fit your needs. Having an open and well-documented API makes this process easier.
**********
Thank you so much to everyone who has read our article! We will definitely explore how to use CDN solutions with popular CMS platforms in the future!